Calculating Energy Of A Wave
How to calculate moving ridge energy
Table of Contents
- Definition
- Formula
- Periodic moving ridge instance
- Random wave example
- Calculator
- References
Definition
Moving ridge free energy is the free energy produced by wind waves in the oceans and ocean due to the motion of water. A car that tin harvest wave free energy is chosen a WEC (Wave Energy Converter).
Waves are formed due to the interaction between the air current passing over the surface of the sea water. As long equally the waves propagate slower than the wind speed but higher up the waves, there is an energy transfer from the wind to the sea waves.
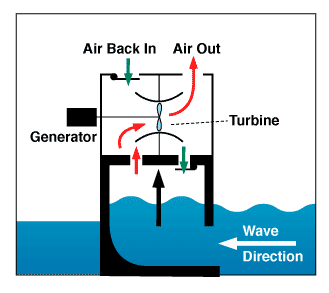
Image: Wave energy
Go back
Formula
There are two types of waves for which we tin can calculate free energy [5]:
- periodic waves (defined as waves which are generated in a specific periodic pattern, east.g. 1 moving ridge each 10 seconds)
- random waves (waves that generated randomly)
Wave free energy is a specific free energy and it'southward calculated pe unit of measurement of horizontal area [J/one thousand2].
The formula (equation) to summate wave power is [5]:
Eastpw = (1/8) · ρ · one thousand · H2 m0
(1)
Erw = (1/16) · ρ · g · Htwo m0
(ii)
where:
- Eastpw [J/chiliad2] – periodic moving ridge energy density
- Eastrw [J/m2] – random wave energy density
- ρ [kg/thousandiii] – water density, equal to 1000 kg/k3
- g [1000/s2] – gravitational acceleration, equal to ix.81 chiliad/s2
- Hm0 [thou] – pregnant wave height
The meaning wave peak is divers as the mean wave pinnacle (trough to crest) of the highest 3rd or fourth of the waves. The unit of wave energy is joule per square meter [J].
Go back
Periodic wave example
Calculate the theoretical energy density of periodic waves with a pregnant moving ridge elevation of v anxiety.
Step i. Catechumen the wave summit from [ft] to [g], by dividing the [ft] value to 3.281:
Footstep 2. Calculate the moving ridge energy density using equation (one):
Epw = (one/8) · yard · 9.81 · 1.524ii = 2848.06 J/m2
Go back
Random wave example
Calculate the theoretical free energy density of random waves with a significant wave height of 7 feet.
Pace one. Convert the wave height from [ft] to [m], by dividing the [ft] value to three.281:
Step 2. Calculate the wave free energy density using equation (2):
Erw = (i/16) · 1000 · 9.81 · ii.13352 = 2790.836 J/m2
Go back
Calculator
The wave free energy figurer allows you to calculate the specific wave energy using the equations divers above. You demand to enter the type of wave, meaning wave height and choose the desired unit of measurement of measurement. The gravitational acceleration is causeless to be 9.81 [m/s2] and water density 1000 [kg/one thousand3].
The default unit for energy is Joule. If you want the result displayed in another unit, use the dropt downwards list to choose and click the Calculate push button again.
Go back
References
[one] David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker, Fundamentals of Physics, 7th edition, John Wiley & Sons, 2004.
[2] Benjamin Crowell, Light and Matter – Physics, 2007.
[3] Raymond A. Serway and John West. Jr. Jewett, Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 6th edition, Brooks/Cole Publishing Co.,2004
[4] Jiansong Li, Jiyun Zhao, and Xiaochun Zhang, A Novel Energy Recovery System Integrating Flywheel and Flow Regeneration for a Hydraulic Excavator Boom Organization, Energies 2020.
[5] Leo H. Holthuijsen, Waves in oceanic and coastal waters, Cambridge University Printing, 2007.
[half-dozen] Kira Grogg, Harvesting the Current of air: The Physics of Wind Turbines, Carleton College, 2005.
Calculating Energy Of A Wave,
Source: https://x-engineer.org/wave-energy/
Posted by: thorntontheinglee.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Calculating Energy Of A Wave"
Post a Comment